Sophos, a global leader in next-generation cybersecurity, today announced the findings of its global survey, “Phishing Insights 2021,” which reveals that phishing attacks targeting organizations ramped up considerably during the pandemic, as millions of employees working from home became a prime target for cybercriminals.
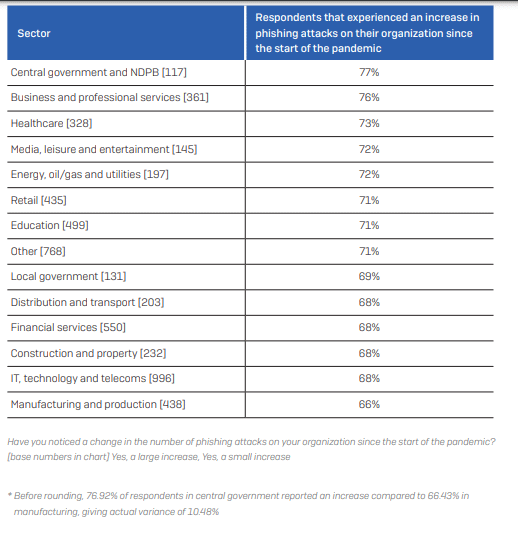
The majority (66%) of IT teams in Nigeria said the number of phishing emails targeting their employees increased during 2020.
“Phishing has been around for over 25 years and remains an effective cyberattack technique. One of the reasons for its success is its ability to continuously evolve and diversify, tailoring attacks to topical issues or concerns, such as the pandemic, and playing on human emotions and trust,” said Chester Wisniewski, principal research scientist at Sophos. “It can be tempting for organizations to see phishing attacks as a relatively low-level threat, but that underestimates their power. Phishing is often the first step in a complex, multi-stage attack. According to Sophos Rapid Response, attackers frequently use phishing emails to trick users into installing malware or sharing credentials that provide access to the corporate network.”
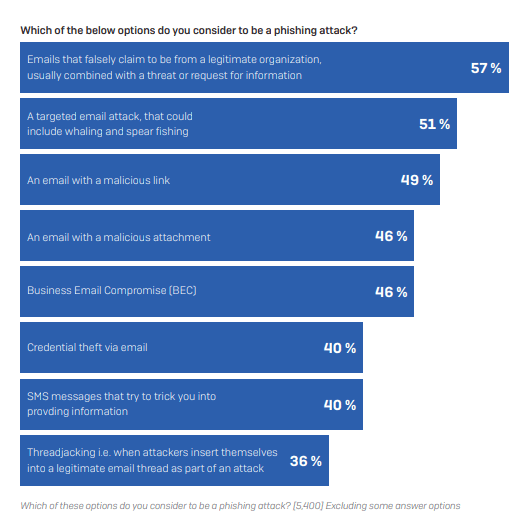
The findings also reveal that there is a lack of common understanding about the definition of phishing. For instance, 55% of IT teams in Nigeria associate phishing with emails that falsely claim to be from a legitimate organization, and which are usually combined with a threat or request for information. Forty-five percent consider Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks to be phishing, and more than one-third (34%) think threadjacking – when attackers insert themselves into a legitimate email thread as part of an attack – is phishing.
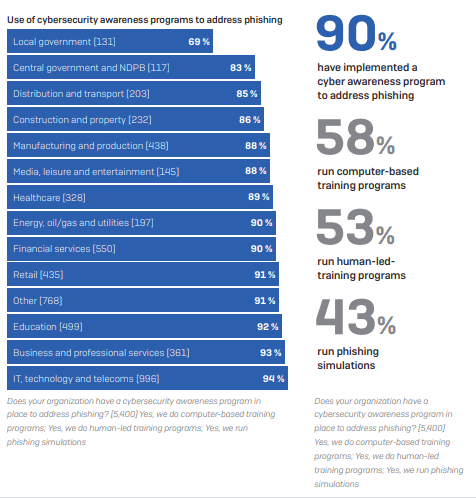
The good news is that most organizations in Nigeria (86%) have implemented cybersecurity awareness programs to combat phishing. Respondents said they use computer-based training programs (55%), human-led training programs (39%), and phishing simulations (36%).
“The ideal would be to prevent phishing emails from ever reaching their intended recipient,” said Wisniewski. “Effective email security solutions can go a long way towards achieving this, but this should be complemented by alert and primed employees who are able to spot and report suspicious messages before they get any further.”






